The Ultimate Guide to Email Privacy: Protecting Your Digital Communications

Loading...

Email privacy has become a critical concern in today's digital landscape, where personal and professional communications face unprecedented threats from surveillance, data mining, and unauthorized access. Understanding email privacy protection is essential for safeguarding sensitive information, maintaining confidential relationships, and preserving your fundamental right to private communication in the digital age. Effective email privacy measures can significantly reduce these risks and provide users with greater control over their digital communications.
Email privacy encompasses more than just keeping your messages secret—it involves protecting metadata, preventing tracking, securing transmission channels, and maintaining control over your personal information. Modern email privacy challenges include corporate surveillance, government monitoring, advertising profiling, and cybercriminal activities that compromise the confidentiality of digital communications. Comprehensive email privacy solutions address these threats through multiple layers of protection and user education.
This comprehensive guide explores the fundamental principles of email privacy, identifies major threats to private communication, and provides actionable strategies for protecting your digital correspondence. Whether you're a business professional handling sensitive information, a privacy-conscious individual, or someone simply seeking to reclaim control over your digital communications, understanding email privacy is crucial for maintaining security and confidentiality. Implementing robust email privacy practices has become essential for anyone who values their digital privacy rights.
The importance of email privacy extends beyond personal preference to encompass legal, professional, and ethical considerations that affect how we communicate in the digital world. Organizations and individuals who prioritize email privacy protect themselves from data breaches, identity theft, targeted harassment, and other serious consequences of compromised communications. Modern email privacy regulations and technologies continue to evolve to meet growing concerns about digital surveillance and data protection.

Email privacy refers to the fundamental principle that electronic communications should remain confidential, accessible only to intended recipients, and free from unauthorized surveillance or data collection. This concept encompasses both the content of email messages and associated metadata, including sender information, recipient details, timestamps, IP addresses, and communication patterns that can reveal personal habits and relationships. Understanding email privacy fundamentals is essential for implementing effective protection strategies. Email privacy encompasses both technical and legal dimensions that users must understand to make informed decisions about their digital communications.
The distinction between email privacy and email security is crucial for understanding comprehensive protection strategies. Email security focuses on preventing unauthorized access to accounts and protecting against malicious attacks, while email privacy addresses the broader concern of limiting data collection, surveillance, and profiling by legitimate service providers, government agencies, and other third parties. Both email privacy and email security are essential components of comprehensive digital communication protection that work together to safeguard user communications.
Modern email privacy challenges involve complex technical and legal considerations that affect how personal information is collected, processed, and shared across digital platforms. Email service providers often collect extensive data about user communications for advertising purposes, analytics, and compliance with government requests, creating significant privacy concerns for users who expect confidential communication. Addressing these email privacy challenges requires both technical solutions and policy reforms.
Privacy-focused email solutions implement various technical measures to protect user communications, including end-to-end encryption, zero-knowledge architecture, metadata protection, and anonymous access options. These technologies ensure that even service providers cannot access message content or detailed information about user communication patterns. Advanced email privacy tools continue to evolve to meet emerging surveillance threats and user needs.
Contemporary email privacy faces numerous challenges from multiple sources, including commercial data mining, government surveillance programs, cybercriminal activities, and inadequate regulatory protections. Major email providers like Gmail, Outlook, and Yahoo routinely scan email content for advertising purposes, creating detailed profiles of user interests, relationships, and behaviors. These practices highlight the urgent need for better email privacy protections and user awareness. The current email privacy landscape requires users to actively seek alternatives and implement protection measures to maintain their communication confidentiality.
Government surveillance programs in many countries collect email communications through various legal and technical mechanisms, including direct access to provider servers, internet traffic interception, and metadata analysis. These activities often occur without user knowledge or consent, creating significant privacy concerns for individuals and organizations worldwide. Protecting email privacy from government surveillance requires both technical measures and legal advocacy.
Cybercriminals exploit email systems through phishing attacks, malware distribution, account compromise, and data theft operations that target both individual users and organizational communications. These threats highlight the importance of comprehensive email privacy strategies that address both technical vulnerabilities and human factors. Effective email privacy protection must account for both legitimate and malicious surveillance threats.
Regulatory frameworks like GDPR, CCPA, and other privacy legislation provide some protection for email communications, but these laws often contain exceptions for national security, law enforcement, and commercial activities that limit their effectiveness. Technical solutions frequently offer stronger privacy protections than legal frameworks alone. Understanding both legal and technical aspects of email privacy is crucial for comprehensive protection.
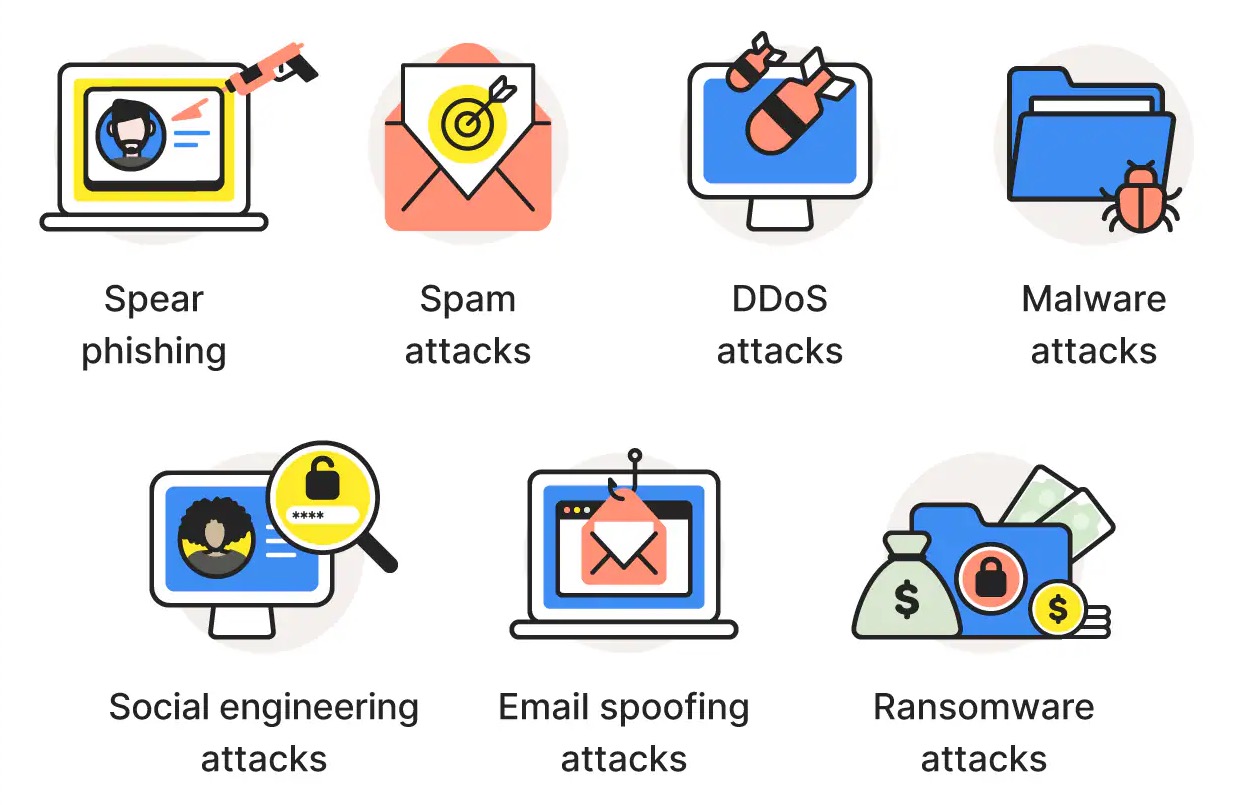
Understanding the diverse threats to email privacy is essential for developing effective protection strategies. These threats range from automated data collection by service providers to sophisticated surveillance operations by government agencies and criminal organizations. Email privacy threats continue to evolve as technology advances and surveillance capabilities become more sophisticated, requiring constant vigilance and adaptation of protection strategies.
Email service providers engage in extensive data collection practices that compromise user privacy through automated scanning, profiling, and targeted advertising systems. Google's Gmail service, for example, analyzes email content to deliver personalized advertisements, build user profiles, and enhance various Google services, creating comprehensive databases of personal information. These practices represent significant challenges to email privacy that users must understand and address. Corporate surveillance of email communications poses one of the most pervasive threats to email privacy in the modern digital landscape.
Commercial email surveillance extends beyond content analysis to include metadata collection, behavioral tracking, contact network mapping, and integration with other data sources. This information is used for advertising targeting, product development, and sometimes shared with third parties through complex data-sharing agreements that users rarely understand or consent to meaningfully. Comprehensive email privacy protection requires understanding these commercial surveillance practices.
Third-party tracking systems embedded in emails monitor user behavior through invisible tracking pixels, link tracking, read receipts, and other surveillance technologies. These systems collect information about when emails are opened, which links are clicked, user location data, and device information, creating detailed profiles of email usage patterns. Blocking these tracking systems is an essential component of email privacy protection.
Email marketing platforms and customer relationship management systems routinely collect and analyze email communication data to optimize campaigns, segment audiences, and track customer interactions. This commercial surveillance infrastructure creates extensive databases of personal information that can be compromised through data breaches or misused for unauthorized purposes. Users concerned about email privacy should carefully review how their data is collected and used by these systems.
Government agencies worldwide operate sophisticated email surveillance programs that collect communications through various legal and technical mechanisms. In the United States, programs like PRISM allow government access to email communications from major providers, while similar programs exist in other countries with varying levels of oversight and transparency. These government surveillance programs represent major threats to email privacy worldwide. Understanding government surveillance capabilities is essential for implementing effective email privacy countermeasures.
Metadata collection by government agencies provides detailed information about communication patterns, relationships, and activities without accessing message content directly. This metadata analysis can reveal sensitive information about personal relationships, political affiliations, business activities, and travel patterns, creating comprehensive profiles of individual behavior. Protecting against metadata surveillance is a critical aspect of email privacy that many users overlook.
International intelligence sharing agreements enable government agencies to access email communications across national boundaries, potentially circumventing domestic privacy protections. These arrangements create complex legal and technical challenges for email privacy protection, particularly for users communicating across international borders.
Court orders, national security letters, and other legal instruments compel email providers to disclose user communications and account information to government agencies. While some providers challenge these requests and implement transparency measures, users often remain unaware of government access to their communications. Strong email privacy requires choosing providers that resist government overreach and implement technical measures to limit data exposure.
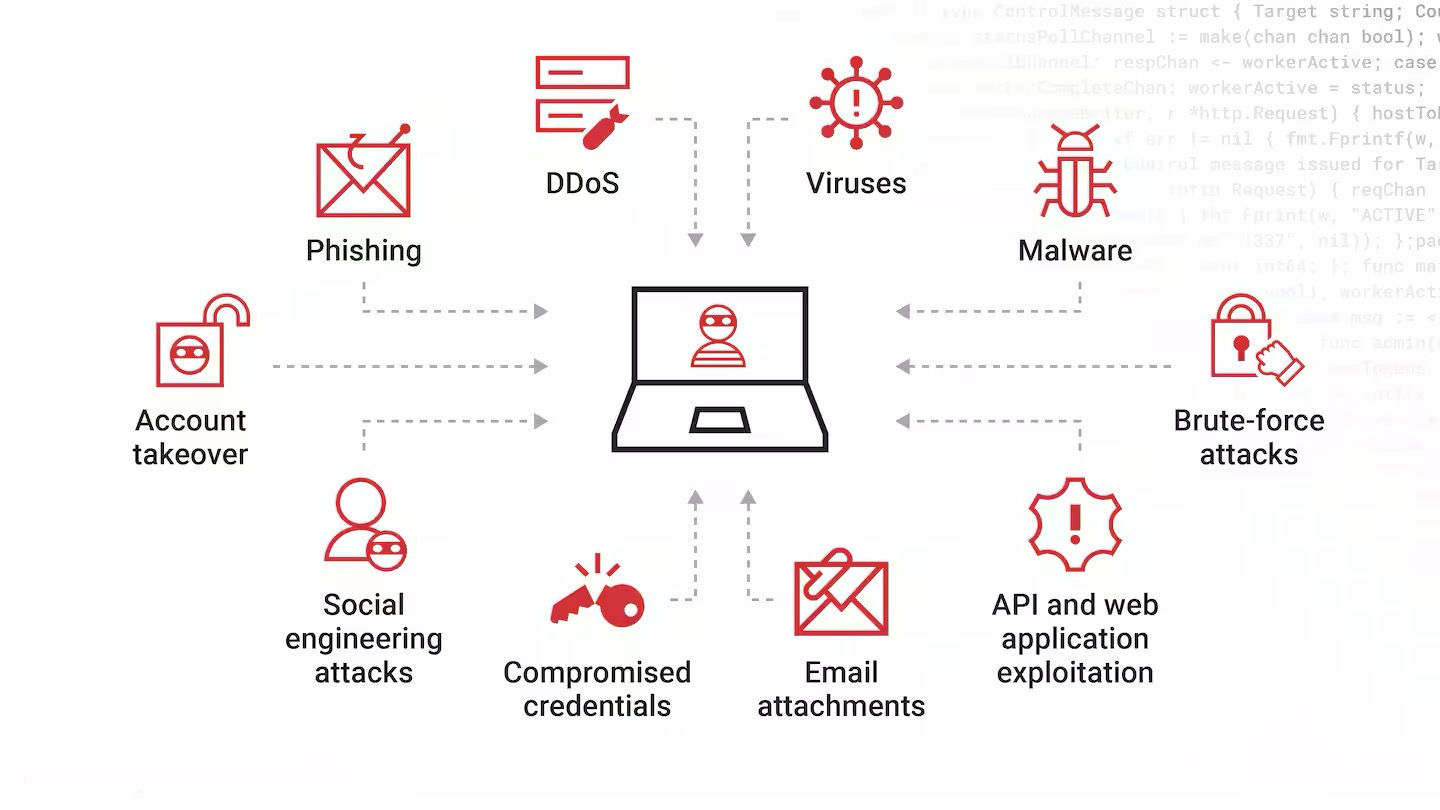
Cybercriminals target email systems through various sophisticated attack methods designed to compromise accounts, steal sensitive information, and exploit communication channels for malicious purposes. Phishing attacks use deceptive emails to trick users into revealing credentials, installing malware, or providing sensitive information that enables further attacks. These criminal activities pose serious threats to email privacy and user security. Cybercriminal exploitation of email vulnerabilities represents a growing challenge to maintaining email privacy and security.
Advanced persistent threat groups and nation-state actors operate sophisticated email surveillance and compromise operations targeting specific individuals, organizations, and industries. These attacks often involve long-term monitoring, credential theft, and data exfiltration that can remain undetected for extended periods. Defending against these advanced threats requires comprehensive email privacy and security measures.
Email account takeover attacks enable criminals to access private communications, steal sensitive information, and use compromised accounts for further malicious activities. These attacks often target high-value individuals and organizations to gain access to confidential information, financial resources, or additional network access. Preventing account takeover is essential for maintaining email privacy and preventing unauthorized access to sensitive communications.
Malware distribution through email remains a significant threat to privacy and security, with criminals using various techniques to deliver ransomware, spyware, and other malicious software that can monitor communications, steal credentials, and compromise entire systems. Protecting against malware is a fundamental requirement for email privacy and overall cybersecurity.
Implementing comprehensive email privacy protection requires a multi-layered approach that addresses technical, behavioral, and service provider considerations. These strategies range from simple configuration changes to complete migration to privacy-focused email services. Effective email privacy protection combines multiple techniques to create robust defense against various surveillance and privacy threats.
Selecting an email provider committed to user privacy represents one of the most effective strategies for protecting email communications. Privacy-focused providers implement technical and policy measures specifically designed to minimize data collection, prevent unauthorized access, and protect user anonymity. Choosing the right provider is a foundational decision for email privacy protection.
ProtonMail leads the privacy-focused email market with end-to-end encryption, zero-knowledge architecture, and strong privacy policies that prevent the provider from accessing user communications. Based in Switzerland, ProtonMail benefits from strong privacy laws and operates under a legal framework that prioritizes user rights over government surveillance requests. ProtonMail represents the gold standard for commercial email privacy solutions.
Tutanota offers similar privacy protections with end-to-end encryption, anonymous account creation, and minimal data collection practices. The German-based provider emphasizes privacy by design and implements quantum-resistant encryption technologies to protect against future cryptographic threats. Tutanota's focus on email privacy makes it an excellent alternative to mainstream providers.
Mailfence provides encrypted email services with additional features like calendar integration, document storage, and key management tools. The Belgian provider operates under European privacy laws and offers both free and premium accounts with varying levels of privacy protection and features. Mailfence combines productivity features with strong email privacy protections.
Other notable privacy-focused providers include Posteo, Mailbox.org, and StartMail, each offering different combinations of privacy features, pricing, and technical capabilities. When selecting a provider, consider factors like encryption implementation, data retention policies, legal jurisdiction, and transparency reporting practices. Evaluating these factors is crucial for choosing the best email privacy solution for your needs.
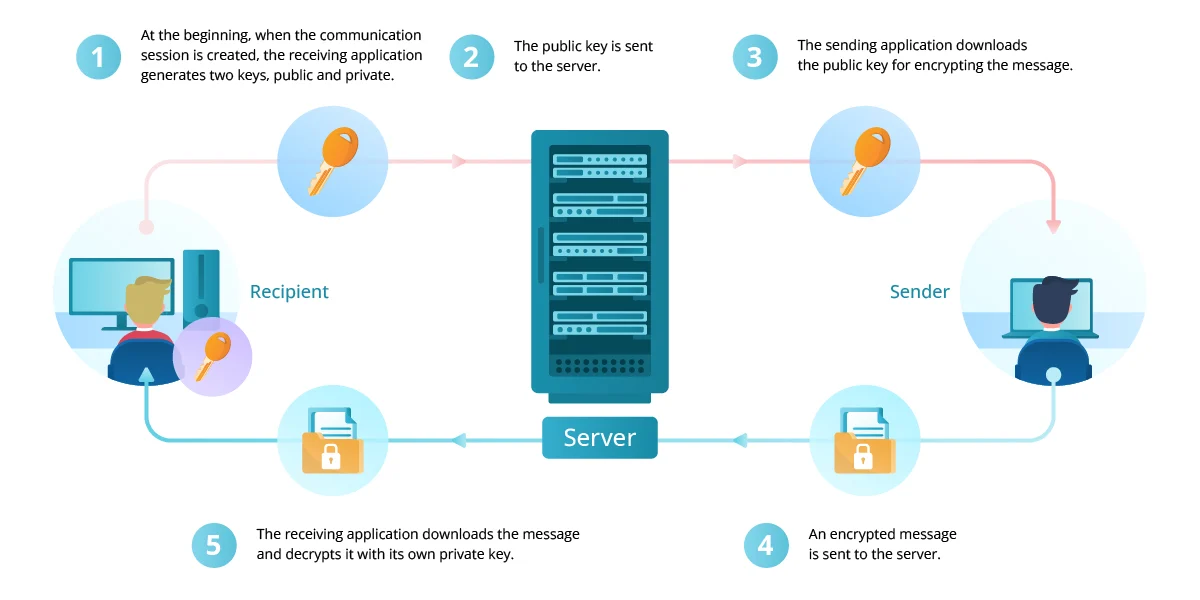
Email encryption provides the fundamental technical foundation for protecting message content from unauthorized access during transmission and storage. End-to-end encryption ensures that only intended recipients can decrypt and read message content, preventing service providers, government agencies, and criminals from accessing private communications. Strong encryption is the cornerstone of effective email privacy protection. Mastering email encryption technologies is fundamental to achieving comprehensive email privacy protection.
PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) and GPG (GNU Privacy Guard) encryption systems provide robust protection for email communications through public-key cryptography. These systems allow users to encrypt messages using recipient public keys and decrypt received messages using private keys, ensuring that only authorized parties can access message content. PGP and GPG remain essential tools for maintaining email privacy in professional and personal communications.
Modern email clients and services increasingly integrate encryption capabilities directly into user interfaces, making strong cryptographic protection more accessible to non-technical users. Services like ProtonMail, Tutanota, and others provide seamless end-to-end encryption without requiring manual key management or complex technical configuration. These user-friendly encryption solutions have made email privacy more accessible to mainstream users.
S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) encryption provides an alternative approach to email encryption that integrates with many existing email systems and organizational infrastructures. While more complex to implement than modern privacy-focused services, S/MIME offers strong encryption capabilities for enterprise and professional environments. Organizations seeking email privacy often implement S/MIME for regulatory compliance and security requirements.
Encryption key management remains a critical consideration for email privacy protection, requiring users to secure private keys, manage key distribution, and maintain access to encrypted communications over time. Privacy-focused email providers often handle key management automatically, while manual encryption systems require more user involvement and technical knowledge. Proper key management is fundamental to maintaining long-term email privacy protection and ensuring continued access to encrypted communications.
Beyond basic encryption and provider selection, advanced email privacy protection involves sophisticated techniques for minimizing metadata exposure, preventing tracking, and maintaining anonymity in digital communications. Advanced email privacy techniques provide additional layers of protection for users with heightened security requirements and threat models.
Email metadata protection addresses the significant privacy risks associated with communication patterns, timing information, and network data that can reveal sensitive information even when message content is encrypted. Advanced privacy techniques focus on minimizing metadata collection and obscuring communication patterns from surveillance systems. Comprehensive email privacy requires protecting both message content and associated metadata. Advanced email privacy practitioners understand that metadata protection is equally important as content encryption.
Anonymous email accounts created without personal identification help protect user identity and prevent correlation between email communications and real-world identity. Using temporary or disposable email addresses for specific purposes further reduces the risk of long-term tracking and profile building. Anonymous accounts are essential tools for maximum email privacy protection.
Tor network integration provides additional anonymity for email communications by routing traffic through multiple encrypted relays that obscure user location and prevent network-level surveillance. Some privacy-focused email providers offer Tor access options, while others can be accessed through Tor browsers for enhanced anonymity. Combining Tor with encrypted email services provides the highest level of email privacy available.
VPN services provide an additional layer of network protection by encrypting internet traffic and masking user location from email providers and network monitors. Combining VPN services with privacy-focused email providers creates multiple layers of protection against various surveillance methods. VPNs are valuable components of comprehensive email privacy strategies.
Email aliasing and forwarding services allow users to create multiple email addresses that forward to a single private account, enabling better organization, spam prevention, and privacy protection. These services help compartmentalize communications and limit exposure of primary email addresses to various services and organizations. Email aliasing is an effective technique for enhancing email privacy without changing providers.
Secure communication practices extend email privacy protection beyond technical measures to include behavioral and operational considerations that minimize privacy risks. These practices help users avoid common privacy pitfalls and maintain consistent protection across different communication scenarios. Implementing comprehensive email privacy practices requires both technical solutions and behavioral changes to maintain effective protection.
Regular security audits of email accounts help identify potential privacy breaches, unauthorized access, and configuration issues that could compromise protection. These audits should include review of account access logs, connected applications, forwarding rules, and privacy settings. Security audits are essential for maintaining effective email privacy over time.
Secure email backup and archival strategies ensure that private communications remain protected when stored for long-term retention. Using encrypted storage solutions and secure backup services helps maintain privacy protection for historical communications. Proper backup strategies are crucial for long-term email privacy protection.
Multi-factor authentication provides essential protection for email accounts by requiring additional verification beyond passwords. Strong authentication helps prevent account compromise that could expose private communications and enable further privacy violations. Multi-factor authentication is a fundamental requirement for email privacy security.
Regular password updates and strong password practices protect email accounts from unauthorized access that could compromise privacy. Using unique, complex passwords and password managers helps maintain account security across multiple services and platforms. Strong password management is essential for maintaining email privacy and account security.
Phishing awareness and social engineering protection help users avoid attacks that could compromise email privacy through credential theft or malware installation. Training and awareness programs help individuals recognize and respond appropriately to various social engineering tactics. Social engineering awareness is essential for maintaining email privacy against human-based attacks.
Ongoing privacy monitoring helps users detect potential threats to email privacy and respond quickly to protect their communications. These monitoring practices include technical measures, service monitoring, and threat intelligence activities. Continuous monitoring is essential for maintaining effective email privacy protection against evolving threats.
Email service transparency reports provide valuable information about government requests, data breaches, and privacy practices that affect user communications. Regular review of provider transparency reports helps users understand the privacy risks associated with their chosen email services. Transparency reports are valuable resources for evaluating email privacy practices and making informed decisions.
Privacy breach notifications and security alerts help users respond quickly to potential threats to their email privacy. Enabling appropriate notifications and monitoring relevant security information sources helps maintain awareness of emerging threats and protection opportunities.
Account activity monitoring helps detect unauthorized access and unusual communication patterns that could indicate privacy compromises. Regular review of account logs and activity reports helps identify potential security incidents before they result in significant privacy violations. Account monitoring is a crucial component of comprehensive email privacy protection strategies.
Third-party privacy audits and security assessments provide independent evaluation of email provider privacy practices and technical implementations. These assessments help users make informed decisions about email service selection and privacy protection strategies. Independent audits are valuable resources for evaluating email privacy claims and choosing trustworthy providers.

Email privacy requirements and protection strategies vary significantly across different usage contexts, including personal communication, professional environments, and specialized use cases that require enhanced privacy protections. Understanding email privacy needs across different contexts is essential for implementing appropriate protection measures and compliance requirements.
Personal email privacy focuses on protecting individual communications from commercial surveillance, government monitoring, and criminal activities. Personal privacy strategies often emphasize ease of use, cost-effectiveness, and integration with existing digital services while maintaining strong protection for sensitive communications. Implementing personal email privacy measures is essential for protecting individual digital rights and communications.
Family and personal relationship communications require special privacy considerations to protect intimate conversations, personal information, and family security. Privacy protection for personal communications should address both technical threats and social risks associated with relationship conflicts, harassment, and stalking. Family communications benefit significantly from robust email privacy protections.
Financial and healthcare communications through email require enhanced privacy protection due to the sensitive nature of this information and potential consequences of exposure. Using encrypted email services and avoiding sensitive information in unencrypted communications helps protect against identity theft and privacy violations. Healthcare and financial email privacy is particularly important due to regulatory requirements and sensitive personal information.
Personal privacy education helps individuals understand email privacy risks and implement appropriate protection measures. This education should cover basic privacy concepts, threat awareness, and practical steps for improving email privacy protection in personal communications. Comprehensive email privacy education empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their digital communications security.
Professional email privacy addresses the complex requirements of business communications, including confidentiality obligations, regulatory compliance, and intellectual property protection. Business email privacy strategies must balance privacy protection with operational requirements and legal obligations. Organizations must prioritize email privacy to protect sensitive business information and maintain competitive advantages.
Client confidentiality and attorney-client privilege communications require the strongest possible privacy protections to maintain legal and ethical obligations. Professional communications often involve legal, financial, and strategic information that requires protection from competitors, regulators, and other parties. Attorney-client email privacy is essential for maintaining legal professional standards and client trust.
Intellectual property and trade secret protection through email privacy helps organizations maintain competitive advantages and comply with confidentiality agreements. Business email privacy strategies should address both internal communications and external correspondence with partners, customers, and suppliers. Protecting intellectual property requires sophisticated email privacy measures to prevent corporate espionage and data theft.
Regulatory compliance requirements for email privacy vary across industries and jurisdictions, including healthcare (HIPAA), financial services (SOX, GLBA), and general data protection (GDPR, CCPA). Organizations must implement email privacy measures that meet applicable regulatory requirements while supporting business operations. Compliance with email privacy regulations is essential for avoiding legal penalties and maintaining business reputation.
Employee privacy rights and organizational monitoring create complex challenges for business email privacy. Organizations must balance legitimate business interests with employee privacy rights while maintaining transparency about monitoring practices and data collection. Workplace email privacy policies must address both legal requirements and employee expectations.
Certain professional roles and activities require enhanced email privacy protection due to the sensitive nature of communications and potential consequences of privacy breaches. These specialized requirements often involve life-safety considerations, legal protections, and ethical obligations. Specialized professions face unique email privacy challenges that require tailored protection strategies.
Journalist and source protection requires sophisticated email privacy measures to protect confidential sources and sensitive information. Journalists must implement strong technical protections and operational security practices to maintain source confidentiality and prevent retaliation or prosecution. Investigative journalism depends heavily on robust email privacy protections to maintain source confidentiality.
Healthcare provider communications involve patient privacy requirements under various regulatory frameworks that mandate specific privacy protections for medical information. Healthcare email privacy must address both patient confidentiality and provider liability concerns. Medical professionals must implement robust email privacy measures to comply with HIPAA and other healthcare regulations.
Legal profession communications require enhanced privacy protection to maintain attorney-client privilege and comply with professional ethics requirements. Legal professionals must implement privacy measures that protect confidential client information and maintain the integrity of legal proceedings. Legal profession email privacy standards are among the highest due to ethical and regulatory requirements.
Human rights and activism communications face enhanced threats from government surveillance, corporate monitoring, and criminal targeting. Activists and human rights workers require sophisticated privacy protection to maintain personal safety and protect vulnerable communities. Human rights organizations must prioritize email privacy to protect activists and vulnerable populations worldwide.

Understanding the legal landscape surrounding email privacy is crucial for implementing effective protection strategies and understanding the limitations of legal protections. Email privacy laws vary significantly across jurisdictions and often provide incomplete protection against various surveillance and data collection activities. Legal frameworks for email privacy continue to evolve as technology and threats advance. Navigating the complex legal landscape of email privacy requires understanding both international regulations and local jurisdiction requirements.
The European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) provides comprehensive privacy protections that affect email communications involving EU residents. GDPR requires explicit consent for data collection, provides rights to data portability and deletion, and imposes significant penalties for privacy violations, creating strong incentives for privacy protection. GDPR represents a significant advancement in legal protections for email privacy worldwide. Understanding GDPR implications is crucial for email privacy compliance in global communications.
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and similar state-level privacy laws in the United States provide limited but growing privacy protections for email communications. These laws typically focus on commercial data collection and provide rights to information, deletion, and opt-out of certain data sharing practices. State-level email privacy laws are expanding to provide stronger protections for users.
National privacy laws in countries like Canada (PIPEDA), Australia (Privacy Act), and others provide varying levels of protection for email communications. Understanding applicable privacy laws helps users understand their rights and available legal remedies for privacy violations. International email privacy laws create a complex but improving landscape for user protection.
International data transfer regulations affect email privacy when communications cross national boundaries, potentially subjecting messages to different legal frameworks and surveillance authorities. Privacy protection strategies should consider the legal implications of international email communications. Cross-border email privacy protection requires understanding multiple legal frameworks and jurisdictional challenges.
Government surveillance authorities vary significantly across countries and often provide broad exceptions to privacy protections for national security, law enforcement, and intelligence activities. Understanding these authorities helps users assess the realistic limitations of legal privacy protections. Government surveillance laws pose significant challenges to email privacy that users must understand and address. Navigating government surveillance laws is essential for realistic email privacy planning and risk assessment.
The USA PATRIOT Act and similar national security legislation in other countries provide government agencies with broad surveillance powers that can override normal privacy protections. These laws often include provisions for secret surveillance, data collection, and provider cooperation requirements that users may never know about. Understanding these surveillance laws is crucial for implementing realistic email privacy protection strategies.
Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act (FISA) courts and similar secret judicial proceedings authorize government surveillance activities that can affect email privacy. These proceedings often occur without user knowledge or meaningful oversight, creating significant gaps in privacy protection. FISA and similar secret court proceedings represent ongoing challenges to email privacy that require vigilant protection measures and policy advocacy.
International intelligence sharing agreements enable government agencies to access email communications across national boundaries, potentially circumventing domestic privacy protections. Understanding these agreements helps users assess the realistic scope of government surveillance threats. International surveillance cooperation creates complex challenges for email privacy that require sophisticated protection strategies.
Email provider privacy policies and terms of service define the contractual relationship between users and providers regarding data collection, use, and sharing practices. Understanding these agreements is essential for assessing the privacy protections provided by different email services. Reading and understanding privacy policies is a fundamental step in protecting email privacy. Corporate privacy policies directly impact email privacy rights and user protection levels.
Data retention policies determine how long email providers store user communications and associated metadata. Shorter retention periods generally provide better privacy protection by limiting the availability of historical communications for surveillance or legal requests. Understanding data retention policies is essential for evaluating email privacy protection levels.
Third-party data sharing agreements often allow email providers to share user information with advertisers, analytics companies, and other commercial partners. Understanding these sharing practices helps users assess the broader privacy implications of their email service choices. Third-party data sharing represents a significant threat to email privacy that users must carefully evaluate.
Transparency reporting by email providers provides valuable information about government requests, data breaches, and privacy practices. Providers that publish regular transparency reports demonstrate greater commitment to user privacy and accountability. Transparency reports are valuable tools for assessing and comparing email privacy practices across different providers.
The future of email privacy will be shaped by advancing technologies, evolving legal frameworks, and changing social expectations about digital privacy. Understanding these trends helps users prepare for emerging privacy opportunities and challenges. The future outlook for email privacy includes both promising technological advances and evolving regulatory frameworks. Email privacy evolution will require ongoing collaboration between technology developers, policymakers, and users to address emerging challenges.
Quantum-resistant encryption technologies are being developed to protect email communications against future quantum computing threats that could break current cryptographic systems. These technologies will become increasingly important as quantum computing capabilities advance and threaten existing encryption methods. Quantum-resistant technologies represent the next evolution in email privacy protection. Future-proofing email privacy against quantum computing threats is essential for long-term communication security. Innovation in email privacy technologies continues to advance protection capabilities against emerging threats.
Decentralized email systems based on blockchain and peer-to-peer technologies offer potential alternatives to centralized email providers that could enhance privacy and user control. These systems aim to eliminate single points of failure and reduce dependence on commercial email providers. Decentralized technologies may revolutionize email privacy by eliminating centralized control and surveillance.
Zero-knowledge proof systems enable email providers to offer services without accessing user data, potentially providing stronger privacy protections than current encrypted email solutions. These technologies allow verification of user identity and message delivery without revealing communication content or metadata. Zero-knowledge systems represent the ultimate goal for email privacy technology development. Zero-knowledge technologies promise to revolutionize email privacy by enabling service provision without data access.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are being applied to both privacy protection and privacy threats, creating an ongoing technological arms race between surveillance and protection capabilities. AI-powered privacy tools may help users better protect their communications while AI-powered surveillance systems become more sophisticated. AI technologies will play an increasingly important role in both protecting and threatening email privacy. The intersection of artificial intelligence and email privacy creates both opportunities and challenges for future protection strategies.
Expanding privacy legislation worldwide is likely to provide stronger legal protections for email communications, though implementation and enforcement remain significant challenges. New laws may address gaps in current privacy protections and provide stronger rights for email users. Future email privacy legislation will likely provide stronger protections but face implementation challenges. Advocacy for stronger email privacy laws is essential for protecting user rights in the digital age.
Government surveillance reform efforts in various countries may limit the scope of surveillance authorities and provide greater oversight of intelligence activities. However, national security concerns often override privacy considerations in legislative processes. Surveillance reform efforts represent hope for improved email privacy protections through legislative changes.
International cooperation on privacy protection may lead to stronger cross-border privacy protections and limitations on surveillance activities. However, conflicting national interests and security concerns complicate international privacy cooperation efforts. International email privacy cooperation is essential for protecting communications across national boundaries. Global coordination on email privacy standards will be crucial for creating consistent protection frameworks worldwide.
Corporate accountability measures may require email providers to implement stronger privacy protections and provide greater transparency about data collection and sharing practices. These measures could significantly improve email privacy protections for mainstream users. Corporate accountability initiatives are driving improvements in email privacy standards and practices across the industry.
Growing privacy awareness among email users is driving demand for better privacy protection and increasing adoption of privacy-focused email services. This trend may force mainstream providers to improve their privacy practices to remain competitive. Increased user awareness is driving significant improvements in email privacy offerings and standards. User education about email privacy rights and options is fundamental to driving market demand for better protection. Enhanced email privacy awareness is transforming user expectations and market demands for better protection.
Generational differences in privacy expectations and technical capabilities will influence the future development of email privacy technologies and services. Younger users who grew up with digital technologies may have different privacy expectations and adoption patterns than older users. Understanding generational differences is important for developing effective email privacy education and adoption strategies. Bridging generational gaps in email privacy understanding is essential for comprehensive protection adoption across all user demographics.
Professional and organizational adoption of privacy-focused email services is increasing as businesses recognize the importance of protecting confidential communications and complying with privacy regulations. This institutional adoption may accelerate the development and improvement of email privacy technologies. Business adoption of email privacy solutions is accelerating due to regulatory and competitive pressures. Enterprise implementation of email privacy measures is becoming a standard requirement for modern business operations.
Privacy-by-design principles are increasingly being incorporated into new email technologies and services, potentially making strong privacy protection the default rather than an optional feature. This shift could significantly improve email privacy for all users. Privacy-by-design represents a fundamental shift toward building email privacy protections directly into system architecture and design processes. The adoption of privacy-by-design principles marks a significant advancement in email privacy implementation across the technology industry.
Email privacy protection is essential for maintaining confidential communications, protecting personal information, and preserving fundamental privacy rights in the digital age. The threats to email privacy are diverse and evolving, requiring comprehensive protection strategies that address technical, legal, and behavioral considerations. Effective email privacy protection has become a fundamental requirement for secure digital communications. Successful email privacy implementation requires ongoing commitment to best practices and continuous adaptation to emerging threats and technologies. Mastering email privacy is crucial for anyone who values confidential digital communications in today's connected world.
Implementing effective email privacy protection requires understanding the threat landscape, selecting appropriate technologies and services, and maintaining consistent security practices. While perfect privacy may be unattainable, significant improvements in email privacy protection are achievable through careful planning and implementation of appropriate measures. Comprehensive email privacy strategies must address multiple threat vectors and evolving technological challenges. Building robust email privacy protection requires a holistic approach that combines technical solutions with user education and awareness.
The future of email privacy will depend on continued technological development, evolving legal frameworks, and growing user demand for privacy protection. Users who take proactive steps to protect their email privacy today will be better positioned to maintain their privacy as threats and technologies continue to evolve. The long-term success of email privacy protection depends on user education, technological advancement, and regulatory support. Advancing email privacy requires collaborative efforts between technology developers, privacy advocates, and policy makers.
By implementing the strategies, technologies, and best practices outlined in this comprehensive guide, individuals and organizations can significantly improve their email privacy protection and maintain greater control over their digital communications. The key to successful email privacy protection lies in taking a comprehensive approach that addresses multiple threat vectors while remaining practical and sustainable for long-term use. Mastering email privacy requires ongoing commitment to learning, implementing, and maintaining effective protection measures. Successful email privacy implementation combines technical expertise with strategic planning and consistent application of best practices. Effective email privacy management ensures long-term protection of sensitive communications and personal information in an increasingly connected digital world.
Looking for more email troubleshooting and management guidance? Check out these related articles:
Discover the complete guide to email templates. Learn how to create, customize, and optimize email templates for sales, marketing, and customer service to save time and boost engagement.
📖 Guides
Master your startup journey with our comprehensive guide. Learn the essential startup journey stages, overcome common startup journey challenges, and develop the startup journey mindset needed to transform your idea into a successful business exit through strategic startup journey planning.
📖 Guides
Master email security with our comprehensive guide. Learn about threats, solutions, best practices, and advanced protection strategies to safeguard your business communications.
📖 Guides